Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 13 abril 2025
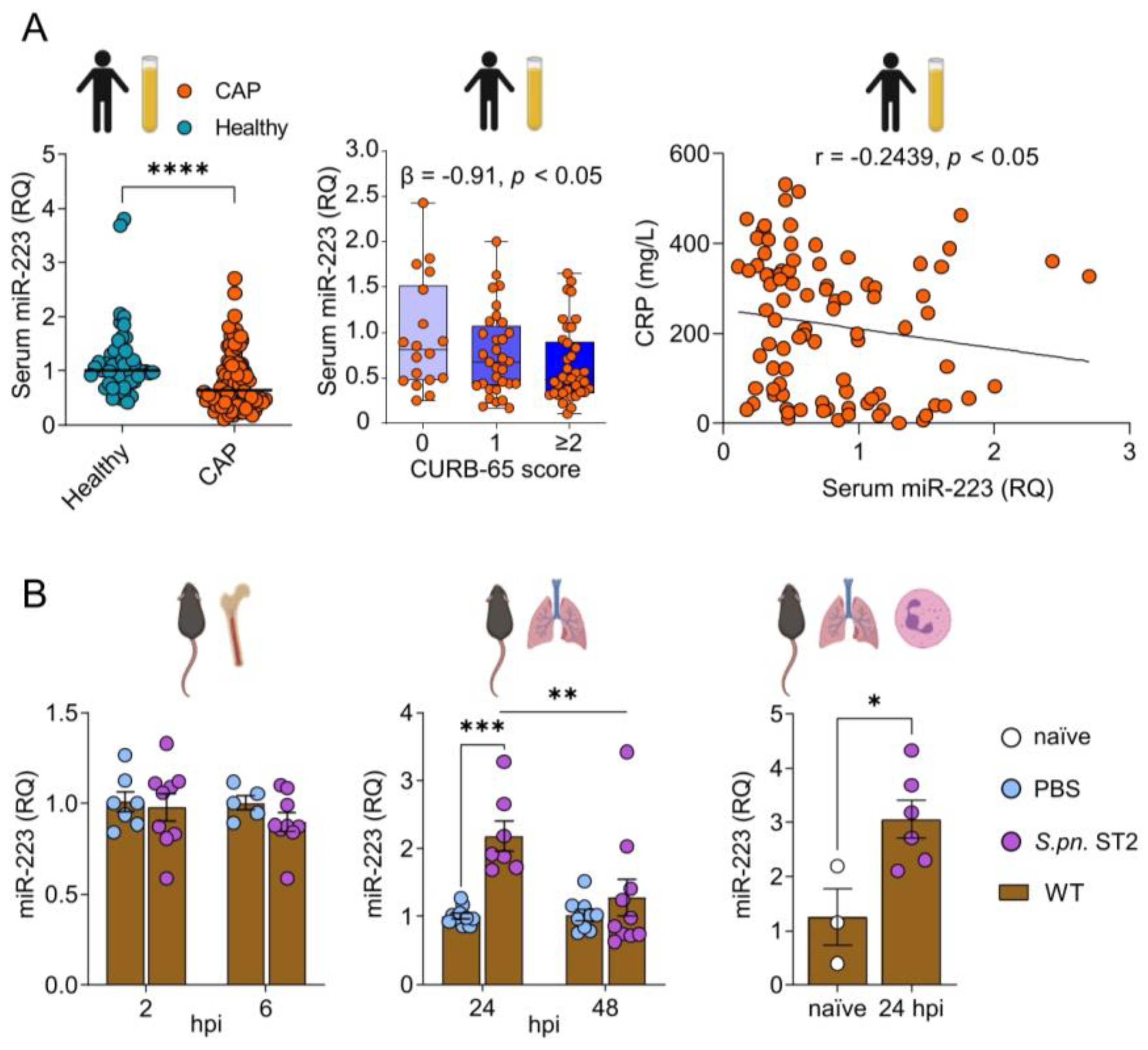
Community-acquired pneumonia remains a major contributor to global communicable disease-mediated mortality. Neutrophils play a leading role in trying to contain bacterial lung infection, but they also drive detrimental pulmonary inflammation, when dysregulated. Here we aimed at understanding the role of microRNA-223 in orchestrating pulmonary inflammation during pneumococcal pneumonia. Serum microRNA-223 was measured in patients with pneumococcal pneumonia and in healthy subjects. Pulmonary inflammation in wild-type and microRNA-223-knockout mice was assessed in terms of disease course, histopathology, cellular recruitment and evaluation of inflammatory protein and gene signatures following pneumococcal infection. Low levels of serum microRNA-223 correlated with increased disease severity in pneumococcal pneumonia patients. Prolonged neutrophilic influx into the lungs and alveolar spaces was detected in pneumococci-infected microRNA-223-knockout mice, possibly accounting for aggravated histopathology and acute lung injury. Expression of microRNA-223 in wild-type mice was induced by pneumococcal infection in a time-dependent manner in whole lungs and lung neutrophils. Single-cell transcriptome analyses of murine lungs revealed a unique profile of antimicrobial and cellular maturation genes that are dysregulated in neutrophils lacking microRNA-223. Taken together, low levels of microRNA-223 in human pneumonia patient serum were associated with increased disease severity, whilst its absence provoked dysregulation of the neutrophil transcriptome in murine pneumococcal pneumonia.

An illustration of the full-duplex cell-free massive MIMO system.
Polimer Program Get File - Colaboratory
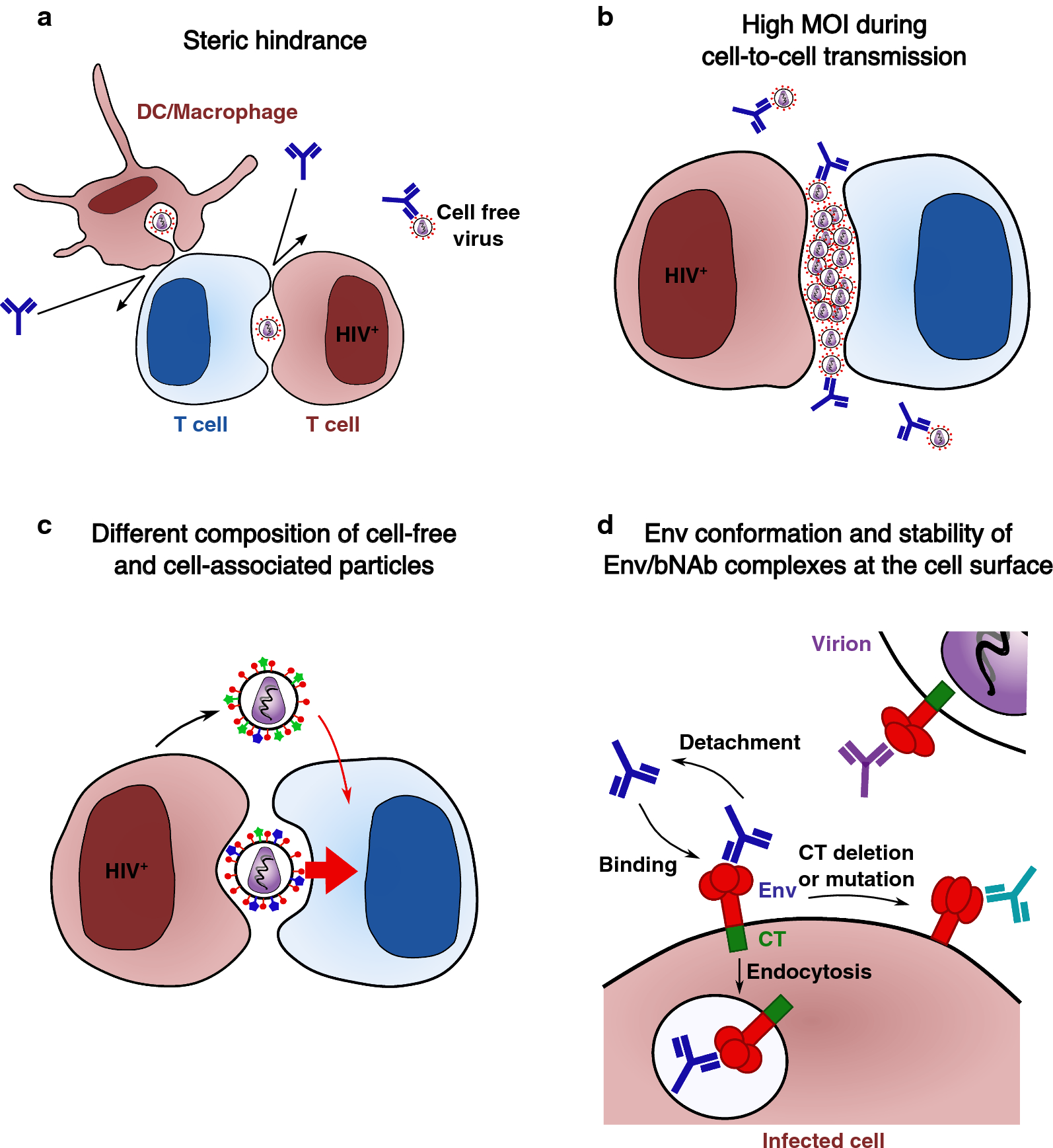
HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies, Retrovirology
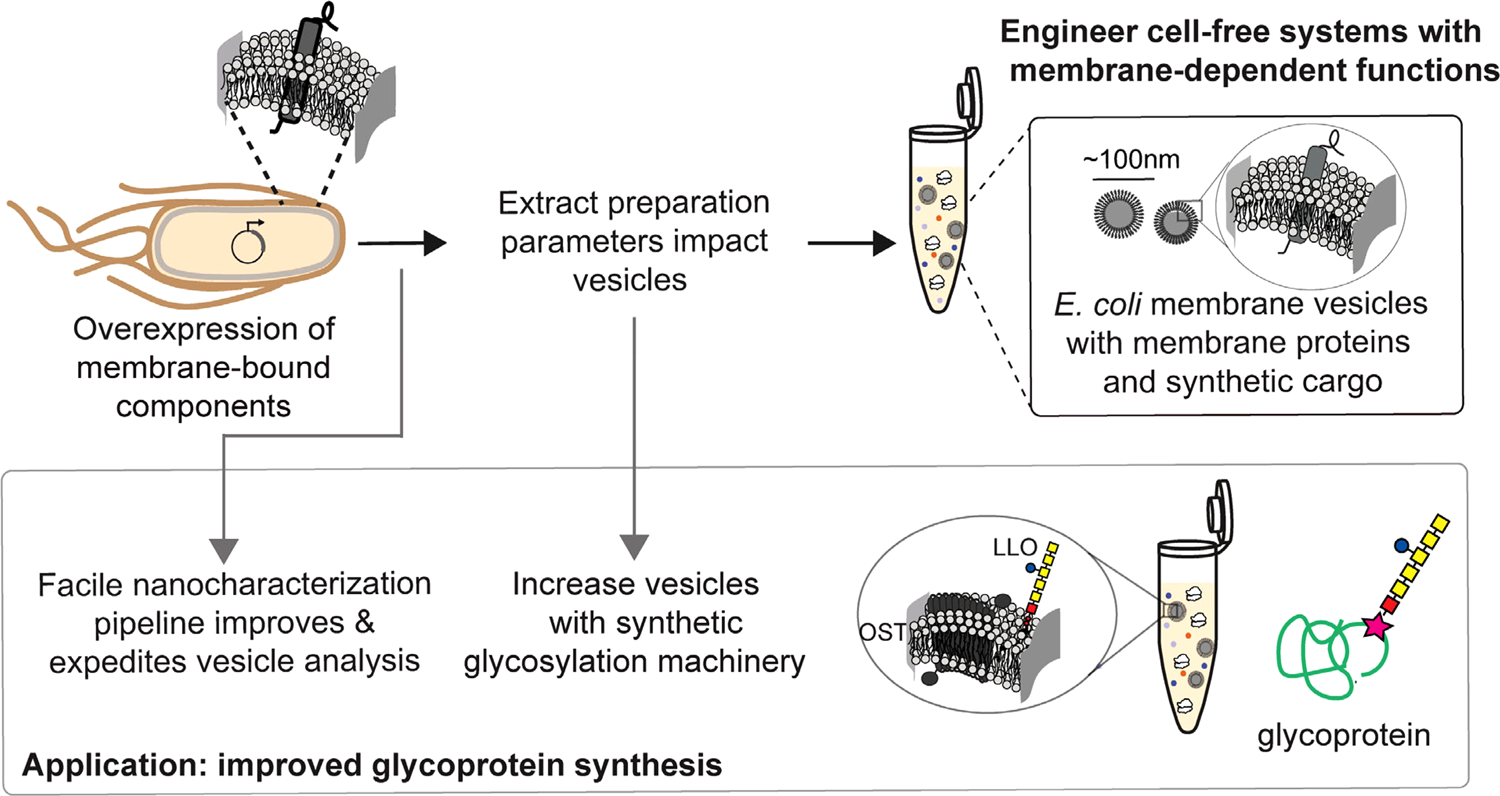
Improving cell-free glycoprotein synthesis by characterizing and enriching native membrane vesicles

Cell-free mutant analysis combined with structure prediction of a lasso peptide biosynthetic protein B2

Advancing synthetic biology through cell-free protein synthesis - ScienceDirect
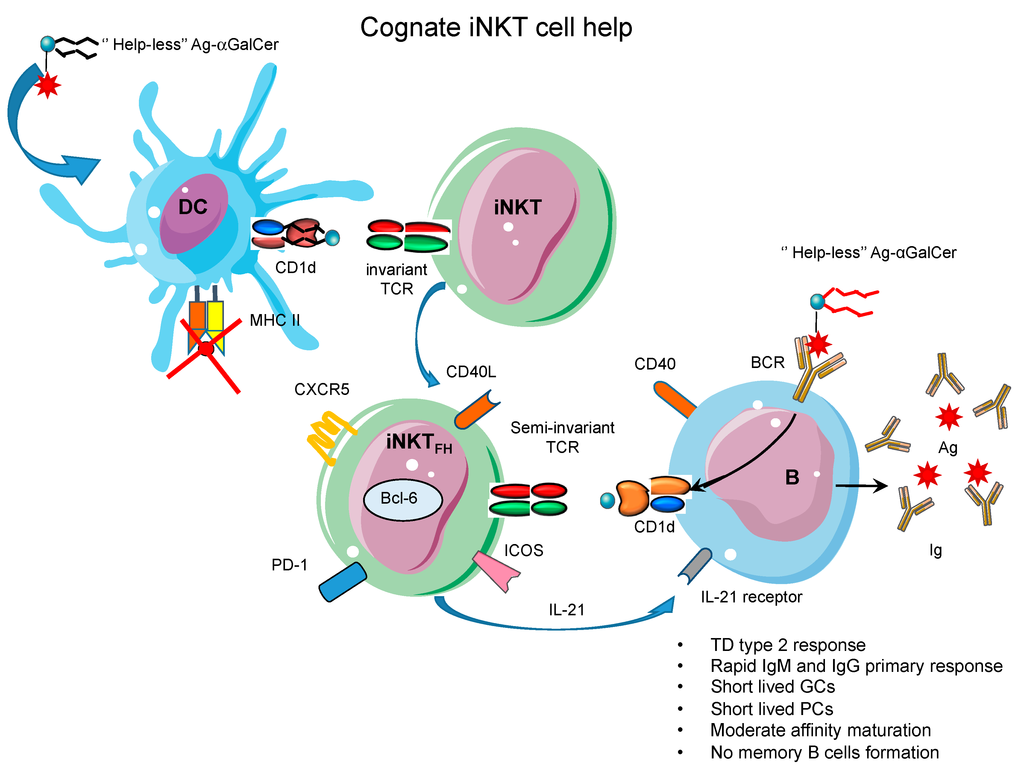
Antibodies, Free Full-Text

Nucleic acid biomarkers of immune response and cell and tissue damage in children with COVID-19 and MIS-C - ScienceDirect

Cell-Free Translation Systems

Cell-free synthetic biology: Engineering in an open world - ScienceDirect
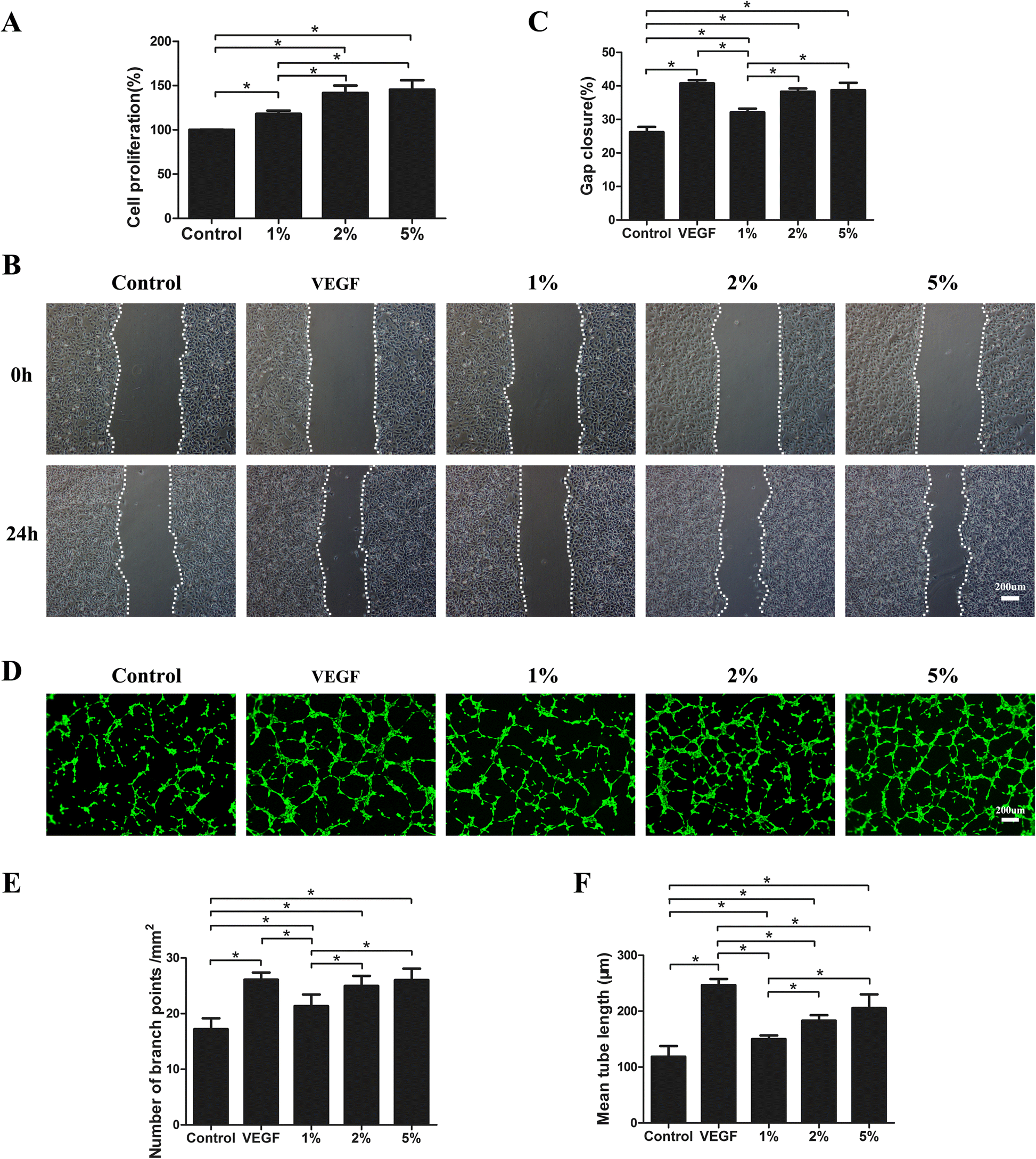
Fat extract promotes angiogenesis in a murine model of limb ischemia: a novel cell-free therapeutic strategy, Stem Cell Research & Therapy

Postbiotics-parabiotics: the new horizons in microbial biotherapy and functional foods, Microbial Cell Factories
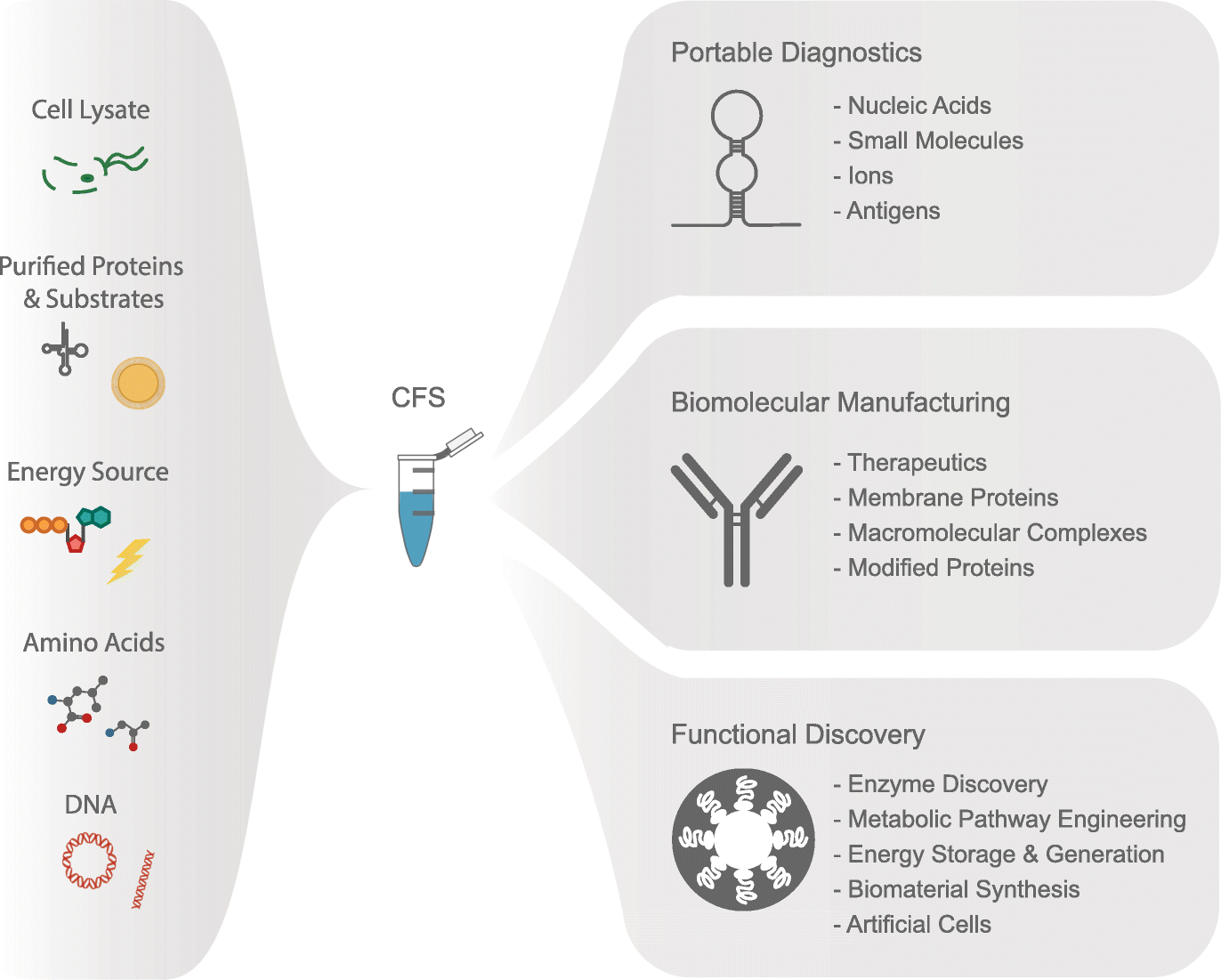
Cells, Free Full-Text
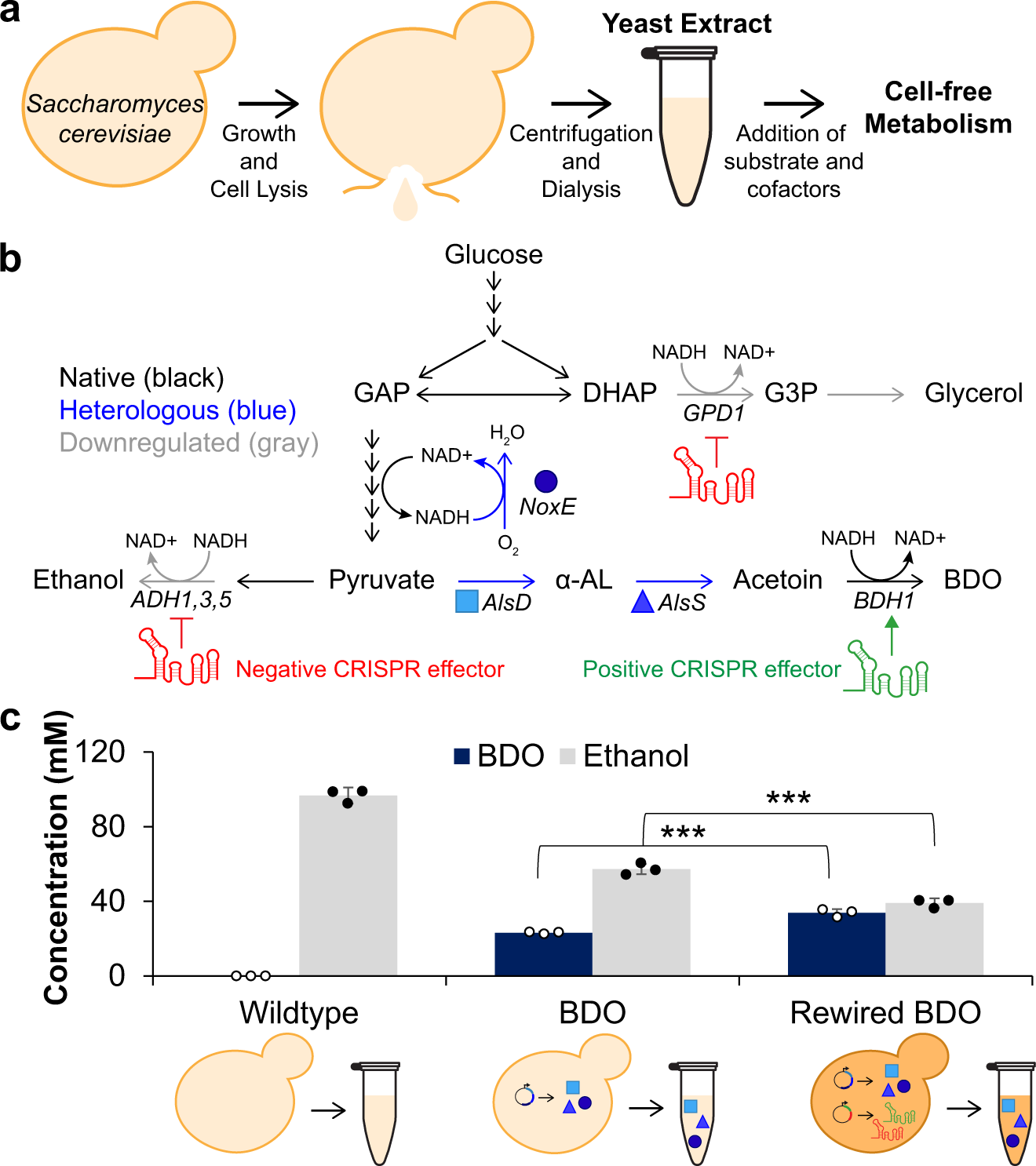
An integrated in vivo/in vitro framework to enhance cell-free biosynthesis with metabolically rewired yeast extracts
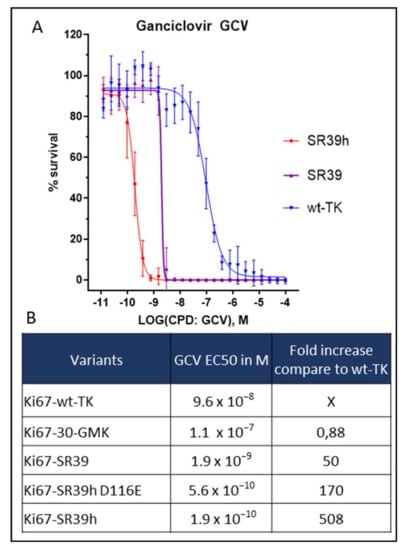
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory
Recomendado para você
-
 Um mergulho na nossa solução13 abril 2025
Um mergulho na nossa solução13 abril 2025 -
Robbyson AeC Interatividade (RST APP) APK for Android - Free Download13 abril 2025
-
 6 problemas que a Robbyson ajuda a resolver com tecnologia de13 abril 2025
6 problemas que a Robbyson ajuda a resolver com tecnologia de13 abril 2025 -
 BizPortal Introduction13 abril 2025
BizPortal Introduction13 abril 2025 -
CONAREC no LinkedIn: #conarec #conarec2023 #customerexperience #cx13 abril 2025
-
 Premium Photo Asian boy dressed in dark blue with a light blue13 abril 2025
Premium Photo Asian boy dressed in dark blue with a light blue13 abril 2025 -
Robbyson Corporate Mobile APK (Android App) - Free Download13 abril 2025
-
 Case Job Caio Luna by Caio Nascimento13 abril 2025
Case Job Caio Luna by Caio Nascimento13 abril 2025 -
 Robbyson Mobile beta 1.4.1 APK Download - Android Productivity Apps13 abril 2025
Robbyson Mobile beta 1.4.1 APK Download - Android Productivity Apps13 abril 2025 -
Robbyson Mobile beta APK (Android App) - Baixar Grátis13 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Love All Play Image by Kaneda Riko #3729391 - Zerochan Anime Image Board13 abril 2025
Love All Play Image by Kaneda Riko #3729391 - Zerochan Anime Image Board13 abril 2025 -
 Página 2, Vetores e ilustrações de Hackear dados para download gratuito13 abril 2025
Página 2, Vetores e ilustrações de Hackear dados para download gratuito13 abril 2025 -
O terra sumô pode ser um potente exercício para coxas e ainda mais par13 abril 2025
-
 Save 33% on The Last of Us™ Part I Digital Deluxe Edition on Steam13 abril 2025
Save 33% on The Last of Us™ Part I Digital Deluxe Edition on Steam13 abril 2025 -
 NOVO TRAILER INÉDITO - DRAGON BALL SUPER: SUPER HERO DUBLADO (LANÇAMENTO) FULL HD - BiliBili13 abril 2025
NOVO TRAILER INÉDITO - DRAGON BALL SUPER: SUPER HERO DUBLADO (LANÇAMENTO) FULL HD - BiliBili13 abril 2025 -
Manga Thrill on X: Goblin Slayer season 2 episode 8 preview! Release date: November 24, 2023 - Title: Heart of Darkness / X13 abril 2025
-
 Aitai☆Kuji Digimon Adventure Tri Music Cafe in Ani On Station Final Party Goods Acrylic Stands13 abril 2025
Aitai☆Kuji Digimon Adventure Tri Music Cafe in Ani On Station Final Party Goods Acrylic Stands13 abril 2025 -
 Toaru Kagaku no Accelerator Episode 12, Toaru Majutsu no Index Wiki13 abril 2025
Toaru Kagaku no Accelerator Episode 12, Toaru Majutsu no Index Wiki13 abril 2025 -
 Papa Louie Pals 2023-10-29-20-07-30 by pavlovskij on DeviantArt13 abril 2025
Papa Louie Pals 2023-10-29-20-07-30 by pavlovskij on DeviantArt13 abril 2025 -
 Rede Raia Drogasil suspende testes de Covid por falta de estoque13 abril 2025
Rede Raia Drogasil suspende testes de Covid por falta de estoque13 abril 2025


