Cells, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 abril 2025
The genus Aspergillus, one of the most abundant airborne fungi, is classified into hundreds of species that affect humans, animals, and plants. Among these, Aspergillus nidulans, as a key model organism, has been extensively studied to understand the mechanisms governing growth and development, physiology, and gene regulation in fungi. A. nidulans primarily reproduces by forming millions of asexual spores known as conidia. The asexual life cycle of A. nidulans can be simply divided into growth and asexual development (conidiation). After a certain period of vegetative growth, some vegetative cells (hyphae) develop into specialized asexual structures called conidiophores. Each A. nidulans conidiophore is composed of a foot cell, stalk, vesicle, metulae, phialides, and 12,000 conidia. This vegetative-to-developmental transition requires the activity of various regulators including FLB proteins, BrlA, and AbaA. Asymmetric repetitive mitotic cell division of phialides results in the formation of immature conidia. Subsequent conidial maturation requires multiple regulators such as WetA, VosA, and VelB. Matured conidia maintain cellular integrity and long-term viability against various stresses and desiccation. Under appropriate conditions, the resting conidia germinate and form new colonies, and this process is governed by a myriad of regulators, such as CreA and SocA. To date, a plethora of regulators for each asexual developmental stage have been identified and investigated. This review summarizes our current understanding of the regulators of conidial formation, maturation, dormancy, and germination in A. nidulans.

Cell-Free Synthetic Biology for Pathway Prototyping - ScienceDirect
Frontiers Combining Cell-Free Protein Synthesis and NMR Into a Tool to Study Capsid Assembly Modulation
Remote immune processes revealed by immune-derived circulating cell-free DNA
Antibodies, Free Full-Text
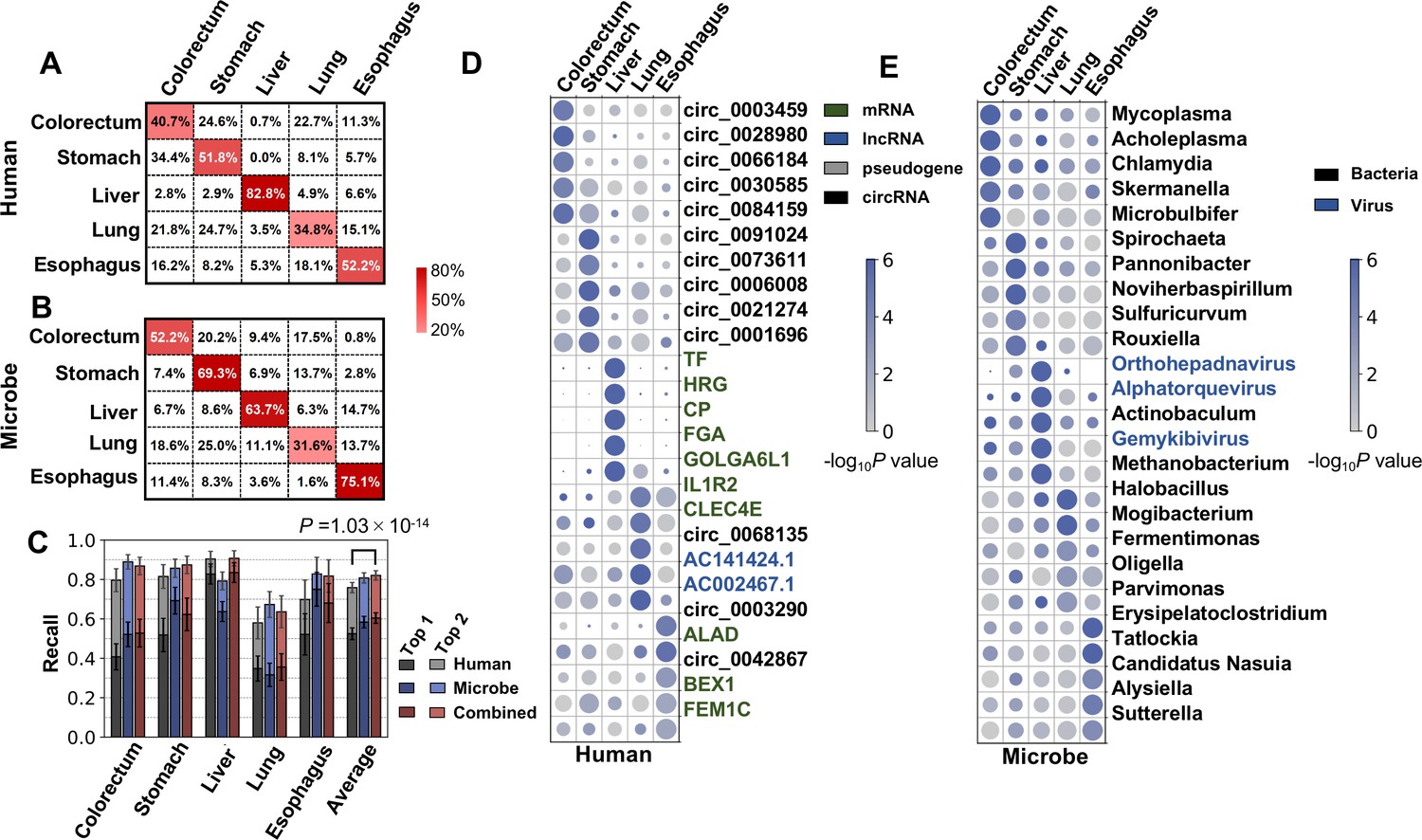
Cancer type classification using plasma cell-free RNAs derived from human and microbes

Cells, Free Full-Text
THE LIVES OF A CELL : LEWIS THOMAS : Free Download, Borrow, and Streaming : Internet Archive
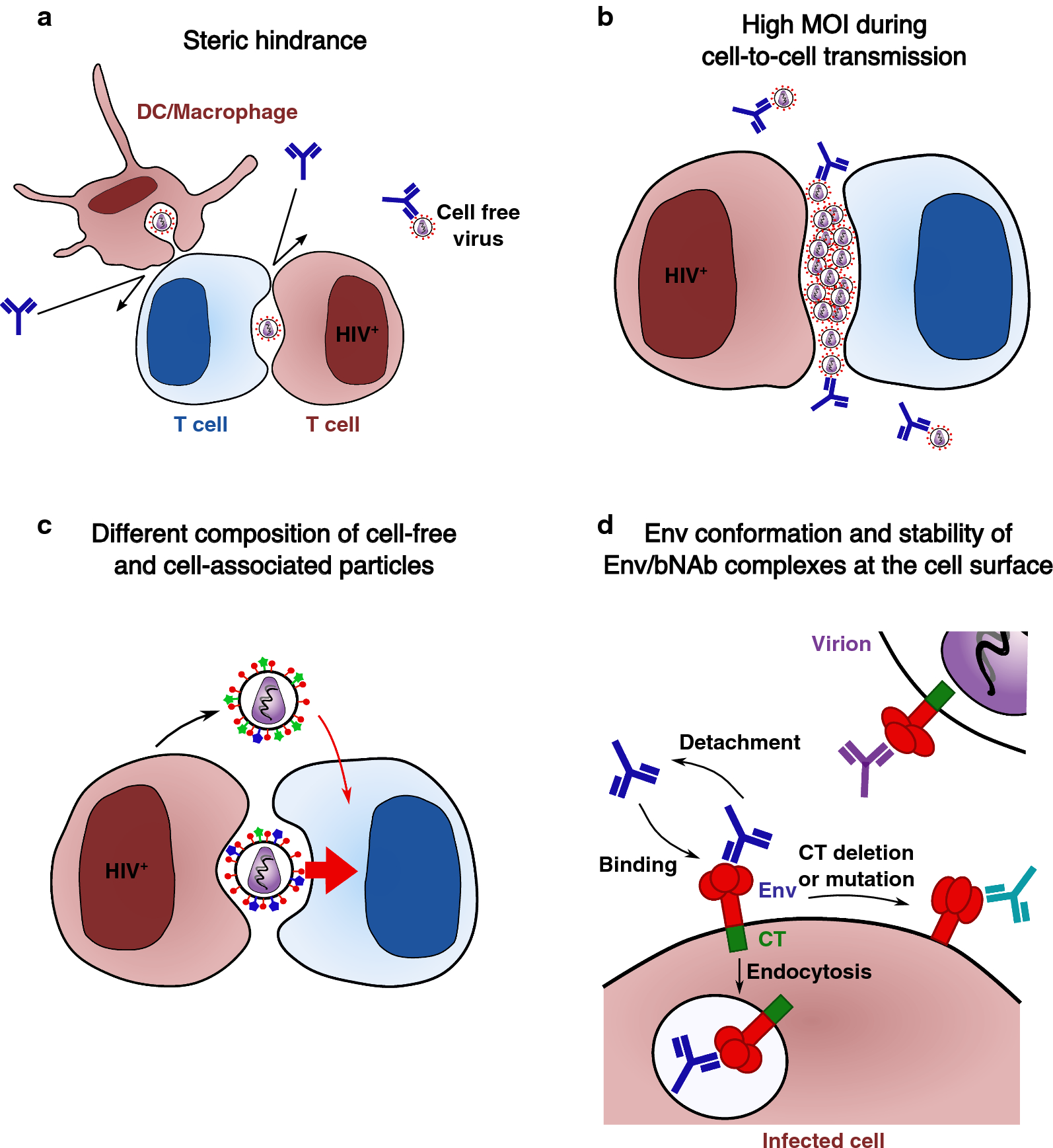
HIV-1 cell-to-cell transmission and broadly neutralizing antibodies, Retrovirology
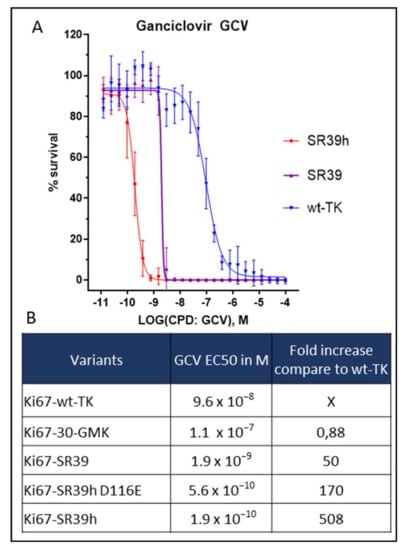
Serial Number Alcohol 120 1.9 6 - Colaboratory
PDF) Protein structural biology using cell-free platform from wheat germ
Recomendado para você
-
 Zoro rebaixado Meme one piece, Imagens de uma peça, Zoro14 abril 2025
Zoro rebaixado Meme one piece, Imagens de uma peça, Zoro14 abril 2025 -
Quem Ganha14 abril 2025
-
 One piece14 abril 2025
One piece14 abril 2025 -
 One Piece Male Base by Q-niffty on DeviantArt14 abril 2025
One Piece Male Base by Q-niffty on DeviantArt14 abril 2025 -
Luffy Face Roblox Item - Rolimon's14 abril 2025
-
Luf Pirate Angry Anime v114 abril 2025
-
 Kuro #Libertação on X: Obviamente não considerei que o maior14 abril 2025
Kuro #Libertação on X: Obviamente não considerei que o maior14 abril 2025 -
 Free transparent luffy png images, page 514 abril 2025
Free transparent luffy png images, page 514 abril 2025 -
 Kurozumi Orochi, One Piece Wiki14 abril 2025
Kurozumi Orochi, One Piece Wiki14 abril 2025 -
 Quanto vc conhece o jimimdabucisuja14 abril 2025
Quanto vc conhece o jimimdabucisuja14 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Minecraft Paper Craft - Four Sets - Utility, Hostile Mobs, Snow Biome, Deluxe14 abril 2025
Minecraft Paper Craft - Four Sets - Utility, Hostile Mobs, Snow Biome, Deluxe14 abril 2025 -
 Tras siete años, Shuumatsu no Harem ha llegado a su final — Kudasai14 abril 2025
Tras siete años, Shuumatsu no Harem ha llegado a su final — Kudasai14 abril 2025 -
Buy Resident Evil 4 Remake - Separate Ways (PC) - Steam Key - GLOBAL - Cheap - !14 abril 2025
-
Pokemon: Trading Post14 abril 2025
-
 Ansatsu Kyoushitsu 2nd Season - Dublado - Anitube14 abril 2025
Ansatsu Kyoushitsu 2nd Season - Dublado - Anitube14 abril 2025 -
 Image 17 of A renegada tragedia lyrica em 3 actos14 abril 2025
Image 17 of A renegada tragedia lyrica em 3 actos14 abril 2025 -
 Coub - The Biggest Video Meme Platform14 abril 2025
Coub - The Biggest Video Meme Platform14 abril 2025 -
 Astrologia cartas de tarô no caminho dos corpos celestes, 7814 abril 2025
Astrologia cartas de tarô no caminho dos corpos celestes, 7814 abril 2025 -
 Teasing Master Takagi-san Movie Shows Off New Trailer - Anime Corner14 abril 2025
Teasing Master Takagi-san Movie Shows Off New Trailer - Anime Corner14 abril 2025 -
 BLU-RAY Cells at Work Official USA Website14 abril 2025
BLU-RAY Cells at Work Official USA Website14 abril 2025


