Psychiatry International, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 abril 2025
Aggressive behaviors of people with dementia pose a significant challenge to employees in nursing homes and aged care facilities. Aggressive behavior is a result of psychomotor agitation in dementia (BPSD). Globally, psychotropic interventions are the preferred treatment for BPSD. However, it is still unclear which psychotropic should be prescribed. The purpose of this systematic review is to compare pharmacological interventions for psychomotor agitation and psychosis symptoms. Method: The studies were extracted from databases, such as PubMed, OVID, and Cochrane, with a date restriction from 2000 to present, and in English. PRISMA steps were used to refine the extracted data. The RCTs extracted for this systematic review compared active ingredient medications to one another or to a placebo. Results: PRISMA was used to assess all selected trials comprehensively. Four trials are being conducted on quetiapine, two on haloperidol, one on olanzapine, three on risperidone, one on brexpiprazole, one on pimavanserin, and two on aripiprazole. Compared to typical antipsychotics, quetiapine showed tolerable adverse effects and did not worsen parkinsonism. Psychosis symptoms and behavioral improvements can be improved with haloperidol. Among elderly patients with psychosis, risperidone reduces angriness, paranoia, and aggression, as well as improves global functioning. As compared with other antipsychotics, aripiprazole provides a lower risk of adverse effects and demonstrated improvement in agitation, anxiety, and depression associated with psychosis. While olanzapine improves hostile suspiciousness, hallucinations, aggression, mistrust, and uncooperativeness, it worsens depression symptoms. Psychosis was treated effectively with pimavanserin without adverse effects on motor functions. Psychosis symptoms are well tolerated by brexpiprazole, but insomnia, headache, and urinary tract infections are common side effects. Conclusions: In this systematic review, we provide an overview of how to choose the correct antipsychotics and dosages for the management of BPSD and emphasize the importance of safe and conservative use of these drugs.

Sylvain Laborde(PhD) - FORTITUDE Mental Training on X: Our last paper with @DrRobertVaughan: A focus on emotional intelligence questionnaires. These questionnaires allow for example to design individualized emotional intelligence training programs

International Journal of School & Educational Psychology - IJSEP

Go Diaper Free: A Simple Handbook for by Olson, Andrea

SOLUTION: Free Online Psychology Course - Studypool
The International Journal of Psychiatry in Medicine: Sage Journals

World Psychiatry

Psychiatry International An Open Access Journal from MDPI

PDF) Pontes, H., Kuss, D. & Griffiths, M.D. (2015). The clinical psychology of Internet addiction: A review of its conceptualization, prevalence, neuronal processes, and implications for treatment. Neuroscience and Neuroeconomics, 4, 11-23.

PDF) Parity of publication for psychiatry

PDF) Social and psychological features of free time organization

Global prevalence and burden of depressive and anxiety disorders in 204 countries and territories in 2020 due to the COVID-19 pandemic - The Lancet
Recomendado para você
-
Brain Test Game Level 287 to 304 Walkthrough, Brain Test Game Level 287 to 304, Brain Test Level 287, 288, 289, 290, 291, 292, 293, 294, 295, 296, 297, 298, 299, 300, 301, 302, 303, 304 Walkthrough, By Dangamevideos14 abril 2025
-
297 brain test|Pesquisa do TikTok14 abril 2025
-
 Brain Test lev.29714 abril 2025
Brain Test lev.29714 abril 2025 -
 Observation Brain Test: If you have 50/50 Vision Find the Number14 abril 2025
Observation Brain Test: If you have 50/50 Vision Find the Number14 abril 2025 -
 brain test 4 level 297 gameplay walkthrough Solution14 abril 2025
brain test 4 level 297 gameplay walkthrough Solution14 abril 2025 -
 Brain Test Level 297 (NEW) Uh! Something is wrong here Answer14 abril 2025
Brain Test Level 297 (NEW) Uh! Something is wrong here Answer14 abril 2025 -
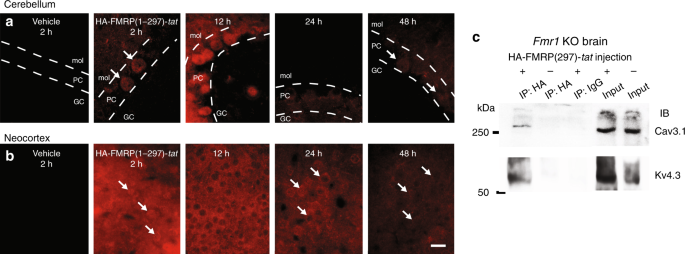 FMRP(1–297)-tat restores ion channel and synaptic function in a14 abril 2025
FMRP(1–297)-tat restores ion channel and synaptic function in a14 abril 2025 -
 NfL as a biomarker for neurodegeneration and survival in Parkinson14 abril 2025
NfL as a biomarker for neurodegeneration and survival in Parkinson14 abril 2025 -
 Scientific breakthrough reveals the ultimate predictor of human14 abril 2025
Scientific breakthrough reveals the ultimate predictor of human14 abril 2025 -
 Frequency of various Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) scores14 abril 2025
Frequency of various Abbreviated Injury Scale (AIS) scores14 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Will Hogwarts Legacy be on Xbox Game Pass? - Charlie INTEL14 abril 2025
Will Hogwarts Legacy be on Xbox Game Pass? - Charlie INTEL14 abril 2025 -
 Neytirix on X: Finally got around to finishing the first part of The Nightmares!! VIDEO >> #FNAF #FANART #digitalart / X14 abril 2025
Neytirix on X: Finally got around to finishing the first part of The Nightmares!! VIDEO >> #FNAF #FANART #digitalart / X14 abril 2025 -
Arifureta Shokugyou de Sekai Saikyou Opening 2 Sheet music for Flute (Solo)14 abril 2025
-
 Duelo: Petrópolis x Teresópolis, na Serra Fluminense14 abril 2025
Duelo: Petrópolis x Teresópolis, na Serra Fluminense14 abril 2025 -
Combo / Kit / Lote 11 Jogos - Ps3 | Jogo de Videogame Jogos Ps3 Originais Nunca Usado 57742312 | enjoei14 abril 2025
-
 Gaara, Wiki14 abril 2025
Gaara, Wiki14 abril 2025 -
 Dragon Ball Z: Budokai Tenkaichi 3 (PS2)14 abril 2025
Dragon Ball Z: Budokai Tenkaichi 3 (PS2)14 abril 2025 -
 FNaF 1 Camera 1B by FuntimeFreddoFazbear on DeviantArt14 abril 2025
FNaF 1 Camera 1B by FuntimeFreddoFazbear on DeviantArt14 abril 2025 -
 Navigating the Marvel Strike Force Reddit Community - HabitBomb14 abril 2025
Navigating the Marvel Strike Force Reddit Community - HabitBomb14 abril 2025 -
 Blueriiot Connect Go: simplificando o monitoramento da sua piscina14 abril 2025
Blueriiot Connect Go: simplificando o monitoramento da sua piscina14 abril 2025


