Biomechanical comparison of different prosthetic materials and posterior implant angles in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 11 abril 2025

The study aimed to evaluate the biomechanical behaviors of different prosthetic materials and posterior implant angles in All-on-4 implant-supported fixed maxillary prostheses with three-dimensional (3D) finite element analysis. The model of complete edentulous maxilla was created using the Rhinoceros and VRMesh Studio programs. Anterior vertical and 17°- and 30°-angled posterior implants were positioned with All-on-4 design. Straigth and angled multi-unit abutments scanned using a 3D scanner. Two different prosthetic superstructures (monolithic zirconia framework and lithium disilicate veneer (ZL) and monolithic zirconia-reinforced lithium silicate (ZLS)) were modeled. Four models designed according to the prosthetic structure and posterior implant angles. Posterior vertical bilateral loading and frontal oblique loading was performed. The principal stresses (bone tissues-Pmax and Pmin) and von Mises equivalent stresses (implant and prosthetic structures) were analyzed. In all models, the highest Pmax stress values were calculated under posterior bilateral loading in cortical bone. The highest von Mises stress levels occured in the posterior implants under posterior bilateral load (260.33 and 219.50 MPa) in the ZL-17 and ZL-30 models, respectively. Under both loads, higher stress levels in prosthetic structures were shown in the ZLS models compared with ZL models. There was no difference between posterior implant angles on stress distribution occurred in implant material and alveolar bone tissue. ZLS and ZL prosthetic structures can be reliably used in maxillary All-on-4 rehabilitation.
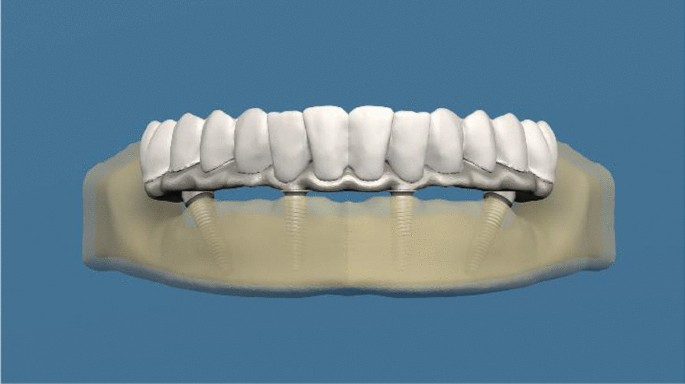
Comparison of stresses in monoblock tilted implants and conventional angled multiunit abutment-implant connection systems in the all-on-four procedure, BMC Oral Health

Effects of Different Positions and Angles of Implants in Maxillary Edentulous Jaw on Surrounding Bone Stress under Dynamic Loading: A Three-Dimensional Finite Element Analysis

Biomechanical comparison of different prosthetic materials and posterior implant angles in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis
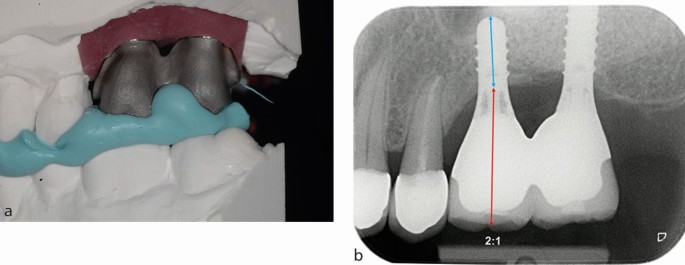
Restoratively driven planning for implants in the posterior maxilla - Part 2: implant planning, biomechanics and prosthodontic planning a proposed prosthodontic complexity index
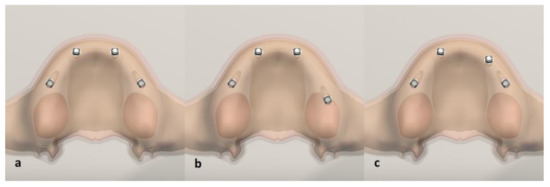
Life, Free Full-Text

Biomechanical comparison of different prosthetic materials and posterior implant angles in all-on-4 treatment concept by three-dimensional finite element analysis

Full article: Biomechanical comparison of implant inclinations and load times with the all-on-4 treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis
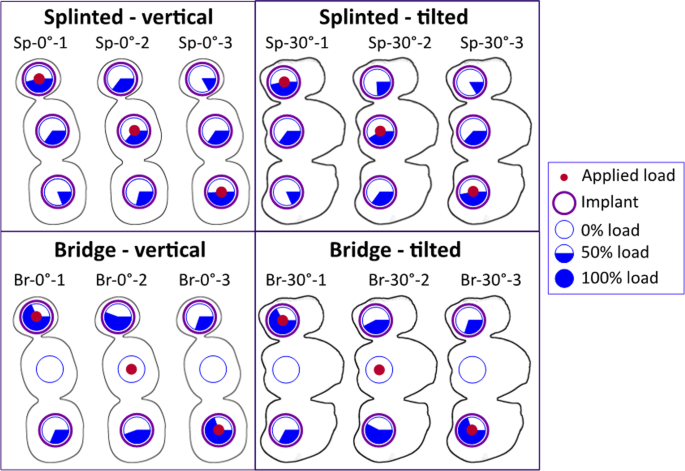
Biomechanical finite element analysis of short-implant-supported, 3-unit, fixed CAD/CAM prostheses in the posterior mandible, International Journal of Implant Dentistry
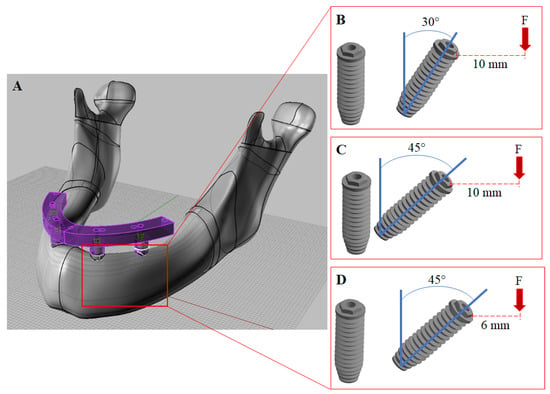
Dentistry Journal, Free Full-Text

Biomechanical comparison of the All-on-4, M-4, and V-4 techniques in an atrophic maxilla: A 3D finite element analysis - ScienceDirect

Full article: The effect of short implants placed in the posterior region on tilted implants in the 'All-On-Four' treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element stress analysis

Biomechanical effects of inclined implant shoulder design in all-on-four treatment concept: a three-dimensional finite element analysis
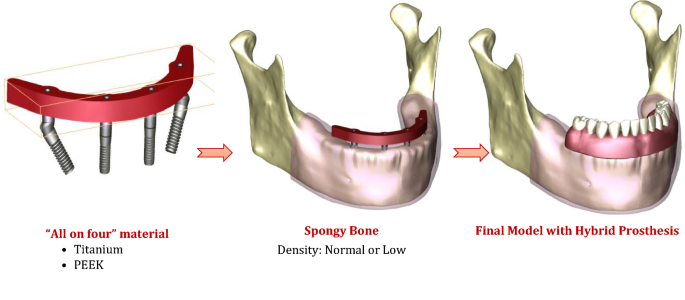
Evaluation of stress and strain on mandible caused using “All-on-Four” system from PEEK in hybrid prosthesis: finite-element analysis

Implant Practice US April/May 2015 Issue - Vol8.2 by MedMark, LLC - Issuu
Recomendado para você
-
Oiles SPB-405030 Box of 4 Straight Bushing - 40 mm ID - IMS Supply11 abril 2025
-
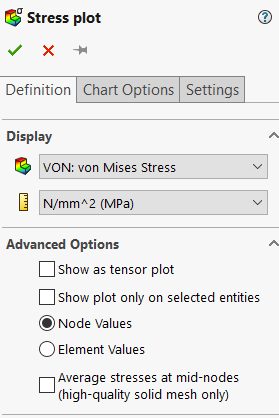 Differences in Node and Element Values for SolidWorks Simulation - IME Wiki11 abril 2025
Differences in Node and Element Values for SolidWorks Simulation - IME Wiki11 abril 2025 -
 Abaqus - Mises Stress values are too high - Student Engineer General Discussion - Eng-Tips11 abril 2025
Abaqus - Mises Stress values are too high - Student Engineer General Discussion - Eng-Tips11 abril 2025 -
Compressive strength of concrete is 28.9 N/mm2 after 56 days. Is this acceptable? - Quora11 abril 2025
-
 The rivet group shown connects two narrow lengths of the plate, one of which carries a 15 kN load positioned as shown. If the ultimate shear strength of a rivet is 35011 abril 2025
The rivet group shown connects two narrow lengths of the plate, one of which carries a 15 kN load positioned as shown. If the ultimate shear strength of a rivet is 35011 abril 2025 -
ST.1943-541X.0001763/asset/b45c3c7f-4d65-4ee0-bfba-8011c75e8660/assets/images/large/figure2.jpg) Flexural Buckling of Hot-Finished High-Strength Steel SHS and RHS Columns, Journal of Structural Engineering11 abril 2025
Flexural Buckling of Hot-Finished High-Strength Steel SHS and RHS Columns, Journal of Structural Engineering11 abril 2025 -
 SOLIDWORKS Simulation Maximum Annotation in Probe Tool11 abril 2025
SOLIDWORKS Simulation Maximum Annotation in Probe Tool11 abril 2025 -
 Materials Dlubal Software11 abril 2025
Materials Dlubal Software11 abril 2025 -
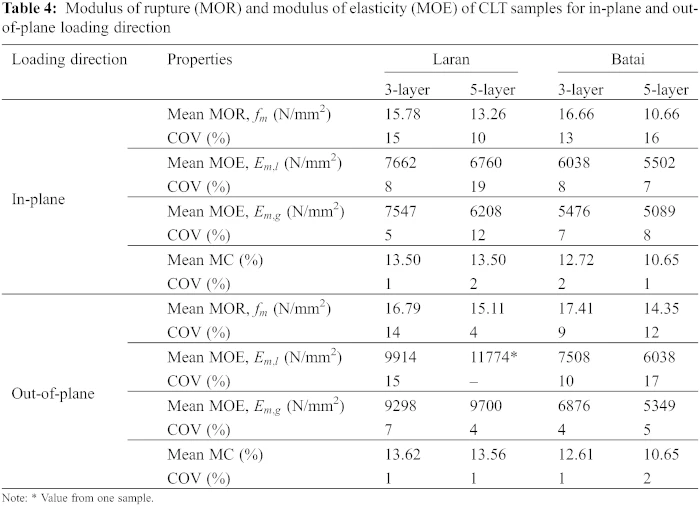 Bending, Compression and Bonding Performance of Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) Made from Malaysian Fast-Growing Timbers11 abril 2025
Bending, Compression and Bonding Performance of Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) Made from Malaysian Fast-Growing Timbers11 abril 2025 -
 i) Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams. (ii) Label and locate the maximum values in terms of P, a, b and L11 abril 2025
i) Draw the shear force and bending moment diagrams. (ii) Label and locate the maximum values in terms of P, a, b and L11 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Caleb, Total Drama Wiki11 abril 2025
Caleb, Total Drama Wiki11 abril 2025 -
 10 best soccer players of all time, from Diego Maradona to Lionel11 abril 2025
10 best soccer players of all time, from Diego Maradona to Lionel11 abril 2025 -
 DIMMU BORGIR / CHROME DIVISION on Instagram: “#espguitars #custom#eclipse# shagrath #unholyroller Photo : Tove/Magicafoto.” in 202311 abril 2025
DIMMU BORGIR / CHROME DIVISION on Instagram: “#espguitars #custom#eclipse# shagrath #unholyroller Photo : Tove/Magicafoto.” in 202311 abril 2025 -
 Khanty World Cup R3 TB: Xiong knocks out Giri11 abril 2025
Khanty World Cup R3 TB: Xiong knocks out Giri11 abril 2025 -
 Roblox coloring pages - ColoringLib11 abril 2025
Roblox coloring pages - ColoringLib11 abril 2025 -
 Quanzhi Fashi – Versatile Mage Capítulo 1000 – Mangás Chan11 abril 2025
Quanzhi Fashi – Versatile Mage Capítulo 1000 – Mangás Chan11 abril 2025 -
 100+ Telekinetic Superhero Names - HobbyLark11 abril 2025
100+ Telekinetic Superhero Names - HobbyLark11 abril 2025 -
 Karakai Jouzu no Takagi-san, AMV11 abril 2025
Karakai Jouzu no Takagi-san, AMV11 abril 2025 -
 It's Go Time! Overwatch 2 is Live Now and Free to Play on Console and PC With New Heroes, Maps, and More11 abril 2025
It's Go Time! Overwatch 2 is Live Now and Free to Play on Console and PC With New Heroes, Maps, and More11 abril 2025 -
 Report Abuse - Dio Hair Png,Kono Dio Da Transparent - free transparent png images11 abril 2025
Report Abuse - Dio Hair Png,Kono Dio Da Transparent - free transparent png images11 abril 2025