Frequency-specific neuromodulation of local and distant
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 14 abril 2025

A growing literature has focused on the brain’s ability to augment processing in local regions by recruiting distant communities of neurons in response to neural decline or insult. In particular, both younger and older adult populations recruit bilateral prefrontal cortex (PFC) as a means of compensating for increasing neural effort to maintain successful cognitive function. However, it remains unclear how local changes in neural activity affect the recruitment of this adaptive mechanism. To address this problem, we combined graph theoretical measures from functional MRI (fMRI) with diffusion weighted imaging (DWI) and repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation (rTMS) in order to resolve a central hypothesis: how do aged brains flexibly adapt to local changes in cortical activity? Specifically, we applied neuromodulation to increase or decrease local activity in a cortical region supporting successful memory encoding (left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex or DLPFC) using 5Hz or 1Hz rTMS, respectively. We then assessed a region’s local within-module degree (WMD), or the distributed between-module degree (BMD) between distant cortical communities. We predicted that (1) local stimulation-related deficits may be counteracted by boosting BMD between bilateral PFC, and that this effect should be (2) positively correlated with structural connectivity. Both predictions were confirmed; 5Hz rTMS increased local success-related activity and local increases in PFC connectivity, while 1Hz rTMS decreases local activity and triggered a more distributed pattern of bilateral PFC connectivity to compensate for this local inhibitory effect. These results provide an integrated, causal explanation for the network interactions associated with successful memory encoding in older adults.

Multiscale model of primary motor cortex circuits predicts in vivo
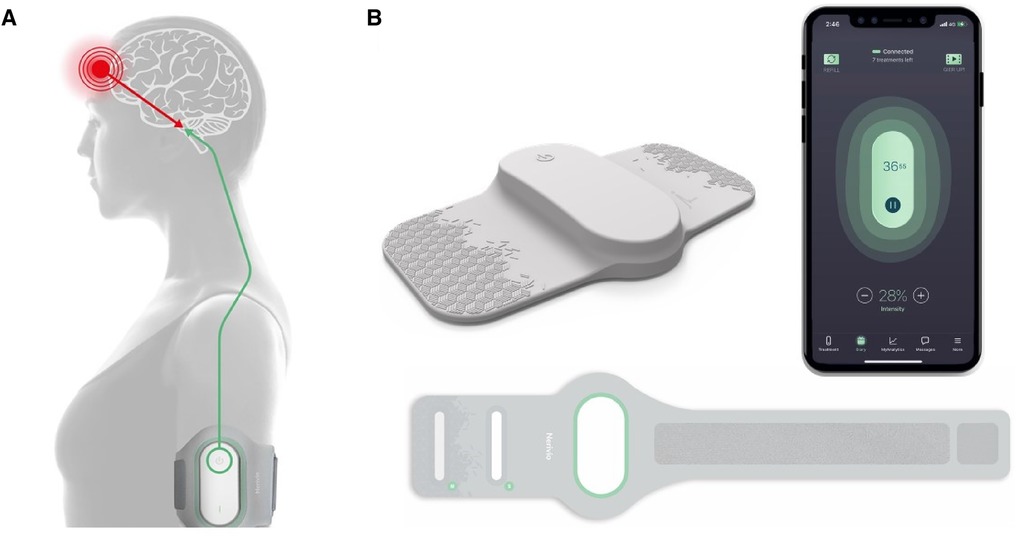
Frontiers Remote electrical neuromodulation (REN) wearable
Ectopic expression of a mechanosensitive channel confers

Table of Contents page: Brain Stimulation: Basic, Translational
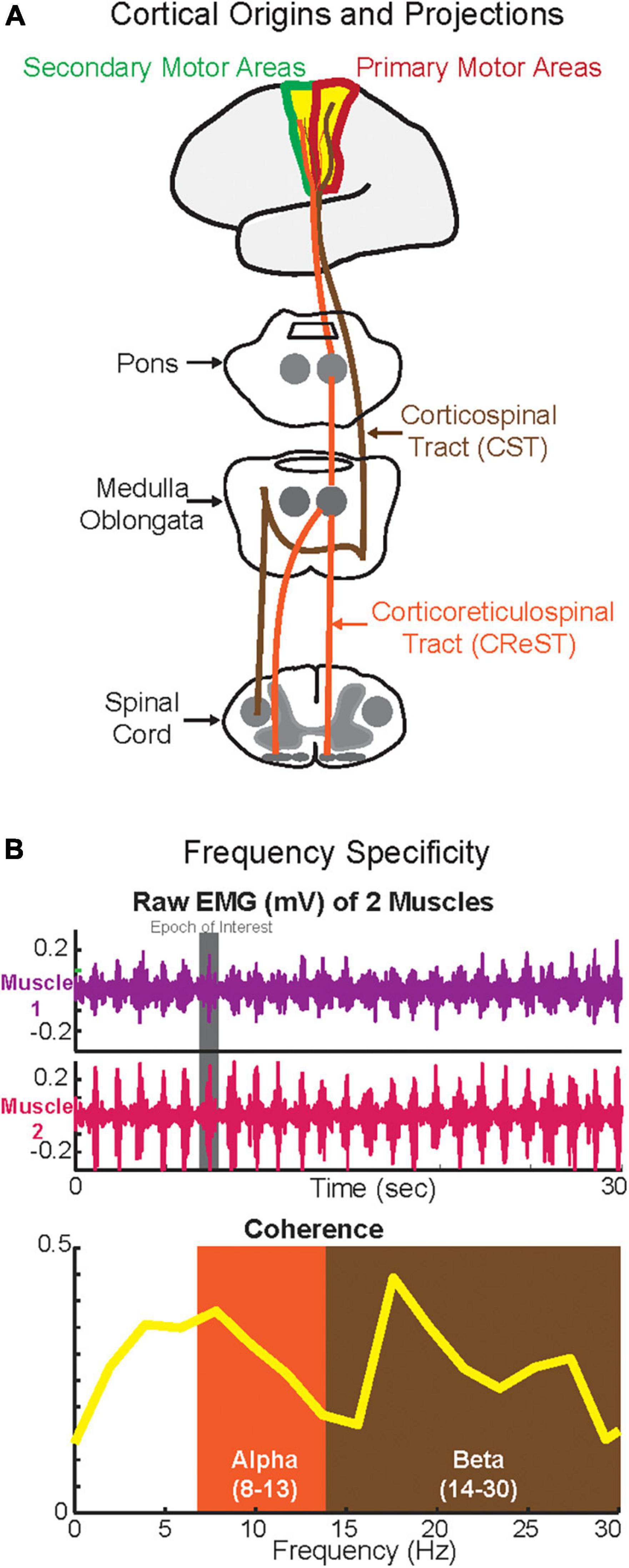
Frontiers Is there frequency-specificity in the motor control of

Biohybrid nanointerfaces for neuromodulation - ScienceDirect
Frontiers Non-contact neuromodulation of the human autonomic

Basic (schematic) circuits involved in the generation of local and

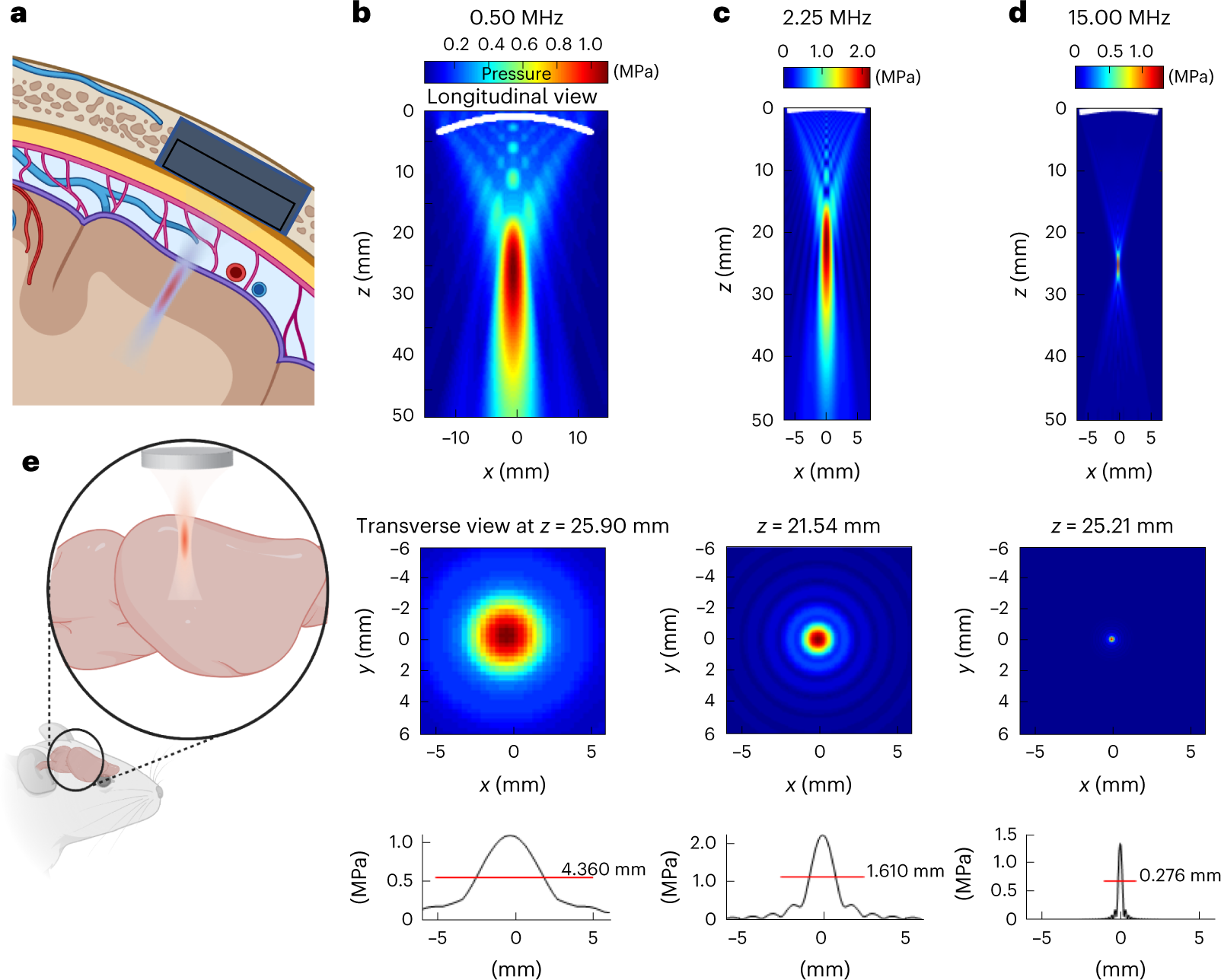
Modelling transcranial ultrasound neuromodulation: an energy-based
Recomendado para você
-
 Brain Test Level 411 (NEW) Light up the birthday candles Answer14 abril 2025
Brain Test Level 411 (NEW) Light up the birthday candles Answer14 abril 2025 -
 como passar do nível 122 do brain test14 abril 2025
como passar do nível 122 do brain test14 abril 2025 -
 MicroRNA-411 and Its 5′-IsomiR Have Distinct Targets and Functions14 abril 2025
MicroRNA-411 and Its 5′-IsomiR Have Distinct Targets and Functions14 abril 2025 -
 Brain Test Tricky puzzles level (411-420)14 abril 2025
Brain Test Tricky puzzles level (411-420)14 abril 2025 -
 Get to Know Our Illustrator: Susie Yi14 abril 2025
Get to Know Our Illustrator: Susie Yi14 abril 2025 -
 Brain Training – Ginger Fox14 abril 2025
Brain Training – Ginger Fox14 abril 2025 -
 208 And 482 In 1 Game Card, Super Combo Game14 abril 2025
208 And 482 In 1 Game Card, Super Combo Game14 abril 2025 -
 Hearing impairment is associated with cognitive decline, brain14 abril 2025
Hearing impairment is associated with cognitive decline, brain14 abril 2025 -
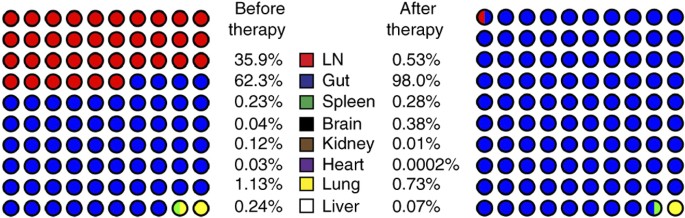 Defining total-body AIDS-virus burden with implications for14 abril 2025
Defining total-body AIDS-virus burden with implications for14 abril 2025 -
Anna Marie Vanderstelt-Frank on Instagram: ❤️Have you ever14 abril 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Cut Last Of Us DLC Nearly Made Ellie's Story Even More Devastating14 abril 2025
Cut Last Of Us DLC Nearly Made Ellie's Story Even More Devastating14 abril 2025 -
 Spider Solitaire APK for Android Download14 abril 2025
Spider Solitaire APK for Android Download14 abril 2025 -
 pic.bstarstatic.com/ugc/5af36c7cf7ea5357b65716c03914 abril 2025
pic.bstarstatic.com/ugc/5af36c7cf7ea5357b65716c03914 abril 2025 -
 KIRBY PATTERNS Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra Case14 abril 2025
KIRBY PATTERNS Samsung Galaxy S22 Ultra Case14 abril 2025 -
 G3 University: Rock Climbing In Taiwan At Long Dong (龍洞) – G3 Store USA14 abril 2025
G3 University: Rock Climbing In Taiwan At Long Dong (龍洞) – G3 Store USA14 abril 2025 -
 tradução fogue mom biz14 abril 2025
tradução fogue mom biz14 abril 2025 -
 Hardest Game Ever 2 by Orangenose Studios14 abril 2025
Hardest Game Ever 2 by Orangenose Studios14 abril 2025 -
 Pin by Xavier A. on sonic the hedgehog14 abril 2025
Pin by Xavier A. on sonic the hedgehog14 abril 2025 -
 Conferences & Events14 abril 2025
Conferences & Events14 abril 2025 -
 Pintando com os Dedos Coloring books, Printable string art patterns, Finger painting14 abril 2025
Pintando com os Dedos Coloring books, Printable string art patterns, Finger painting14 abril 2025
